Understanding Scarring: An Overview
Scarring is a natural part of the body’s healing process, resulting from the repair of damaged skin or tissue.
It can occur after injuries, surgeries, or skin conditions, and the appearance of scars can vary widely. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of scarring, exploring its nature, types, treatment options, and prevention strategies for managing scars effectively.
Identifying the Types of Scarring
Scars can manifest in different forms, including:
- Keloid Scars: Raised, thickened scars that extend beyond the original wound area.
- Hypertrophic Scars: Similar to keloid scars but confined to the wound’s boundaries.
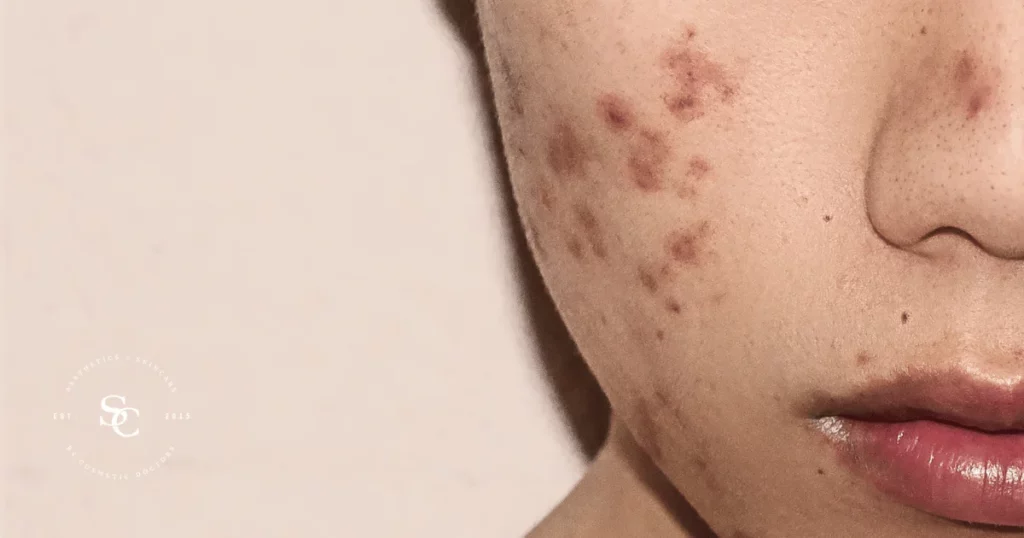
- Atrophic Scars: Indented or depressed scars, often seen in conditions like acne.
- Contracture Scars: Tight, stretched scars that result from burns and can limit movement.
- Stretch Marks: Narrow streaks or lines on the skin, commonly occurring during pregnancy or rapid weight changes.
Causes and Risk Factors of Scarring
Understanding the causes and risk factors of scarring is essential:
- Injuries: Accidents, cuts, and surgical procedures can lead to scarring.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like acne can result in atrophic scars.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence an individual’s tendency to develop certain types of scars.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care during the healing process can impact scar formation.
- Age: The body’s ability to heal and the appearance of scars may change with age.
Diagnosis: How Scarring is Detected
Scarring is typically diagnosed through visual examination by a healthcare provider or dermatologist.
They may assess the scar’s size, texture, and appearance to determine the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Scarring
Several treatment options can help address and improve the appearance of scars:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter or prescription creams, gels, or ointments containing ingredients like silicone, retinoids, or corticosteroids can be applied to scars to reduce their appearance.
- Injections: In some cases, injections of corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, or other substances can help flatten and soften scars.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target and break down scar tissue, promoting the growth of new, smoother skin.
- Surgical Revision: Surgical procedures, such as scar excision or Z-plasty, may be performed to remove or reposition scars.
- Microneedling: This minimally invasive procedure involves the use of a device with tiny needles to stimulate collagen production and improve the texture of scars.
Prevention Strategies for Scarring
Preventing excessive scarring involves adopting strategies during the wound healing process:
- Proper Wound Care: Keep wounds clean, moist, and protected with dressings to promote optimal healing.
- Sun Protection: Shield scars from the sun’s harmful UV rays to prevent them from darkening and becoming more noticeable.
- Avoiding Irritation: Avoid activities or products that may irritate healing wounds.
- Nutrition: Maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and nutrients to support the body’s healing processes.
Home Remedies and Self-Care for Scarring
In addition to medical treatments, there are remedies and self-care practices that may help improve scars:
- Scar Massage: Gently massaging the scar with a moisturizing cream can help break down scar tissue and improve blood circulation.
- Silicone Sheets or Gel: Over-the-counter silicone sheets or gel can be applied to scars to soften and flatten them.
- Onion Extract: Some topical products containing onion extract may help reduce scar redness and thickness.
Impact of Scarring on Self-Image
Scarring can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and body image, especially if scars are prominent or located in visible areas. Addressing scars can improve self-confidence and overall well-being.
Long-Term Management of Scarring
Managing scars often involves ongoing care:
- Skincare Routine: Maintain a consistent skincare routine that includes scar-specific treatments as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Professional Guidance: Regular visits to a dermatologist or plastic surgeon can provide guidance on managing scars effectively.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Incorporate a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and hydration, to support optimal wound healing and scar management.
In conclusion, understanding scarring, its types, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for effectively managing and improving the appearance of scars. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist can provide personalized guidance on the most suitable treatments and management approaches for individual concerns.